While comparing it to the PVC molding process, we will introduce the points to note when molding CPVC (extrusion molding, injection molding, profile extrusion molding) and the recommended settings for the molding machine.
The molding processes for CPVC and PVC are very similar.
CPVC molding processes such as extrusion and injection molding can generally use equipment and tools for PVC molding.
However, it is necessary to set the molding machine appropriately, such as by setting the temperature and screw to match the material characteristics.
The Sekisui Chemical Group is itself a molding manufacturer and has high technological capabilities in the field of molding, including extrusion and injection molding.
In addition to selling CPVC compounds, we can also offer process proposals based on our knowledge as a molding manufacturer.
CPVC Compound (powder, pellet)


Molding (Photo: Extrusion molding)
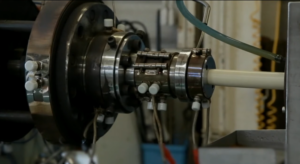

Molded product (pipes, etc.)

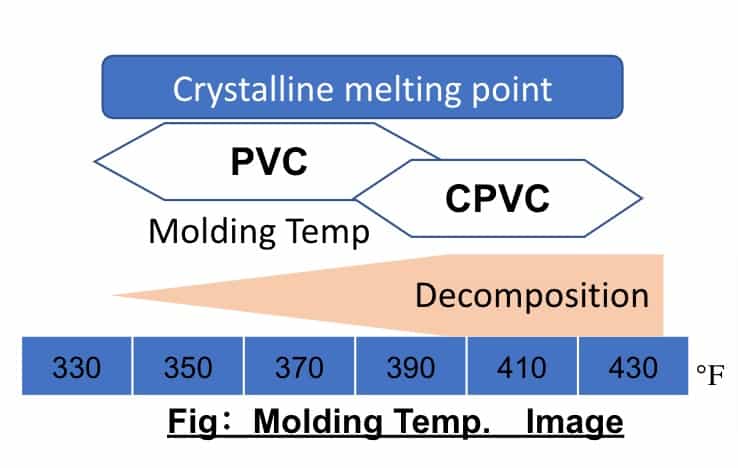
The main differences between PVC and CPVC are thermal stability and viscosity.
CPVC will not melt without the application of moderate heat and will not exhibit excellent physical properties.
On the other hand, it will decompose if exposed to excessively high temperatures.
The diagram on the right is a reference material that shows the crystallization melting points of PVC and CPVC.
PVC and CPVC materials have different thermal stabilities:
In general, the viscosity of CPVC is higher than that of PVC. In the case of PVC, the viscosity (=K-value) is set simply by the degree of polymerisation. In the case of CPVC, on the other hand, the viscosity (=K-value) is set by a combination of degree of polymerisation and chlorination.
PVC and CPVC materials have different thermal stabilities:
The structure of the screw and mould tools is an important factor. Molding equipment must be suitable for CPVC molding.
The screw undergoes shear heating. Temperature control is therefore required to keep the material at the correct temperature.
| PVC | CPVC | |
| Twin-screw extruder | Screw motor:High torque Screw:Parallel φ60-170 Conical φ50-85 | Screw mortar:High torque Screw:Parallel φ60-135 Conical φ50-70 |
| Screw rotation | ー | Lower than PVC |
| Condition (Barrel Temp.) | 300 – 340℉ | 340 – 410℉ |
| Mold type | Stainless steel | Stainless steel Small quantity (flow channel section) Mold angle: acute angle |
| PVC | CPVC | |
| Injection machine | Screw mortar: High torque Barrel cooling: Blower | Screw mortar: High torque Barrel cooling: Blower Barrel zone: 4-5 zone Nozzle: Short nozzle、φ:Larger than PVC |
| Screw rotation | 9-14 m/sec | 8-13 m/sec (lower than PVC) |
| Condition (Barrel Temp.) | 320 – 365℉ | 320 – 392℉ |
| Condition (holding pressure) | 100 – 170 MPa | 100 – 170 MPa |
| Mold type | Stainless steel Gate: Direct gate | Stainless steel Gate: Direct gate |
| PVC | CPVC | |
| Single screw extruder | Single screw machine Screw: Dulmage, Fullfight | Single screw machine Screw: Fullfight recommended (Dulmage) L/D = 22 – 25 Compression ratio: 2.5 – 3.2 |
| Screw rotation | 15~ rpm (65 mm single) | 15–25 rpm (65 mm single) |
| Condition (Barrel Temp.) | 284 – 338℉ | 300 – 370℉ |
| Mold type | Stainless steel | Stainless steel |