- Language
- English
- 日本語
- English (India)
- हिन्दी
- 中文
One of the benefits of CPVC over competitive materials is its superior heat resistance.
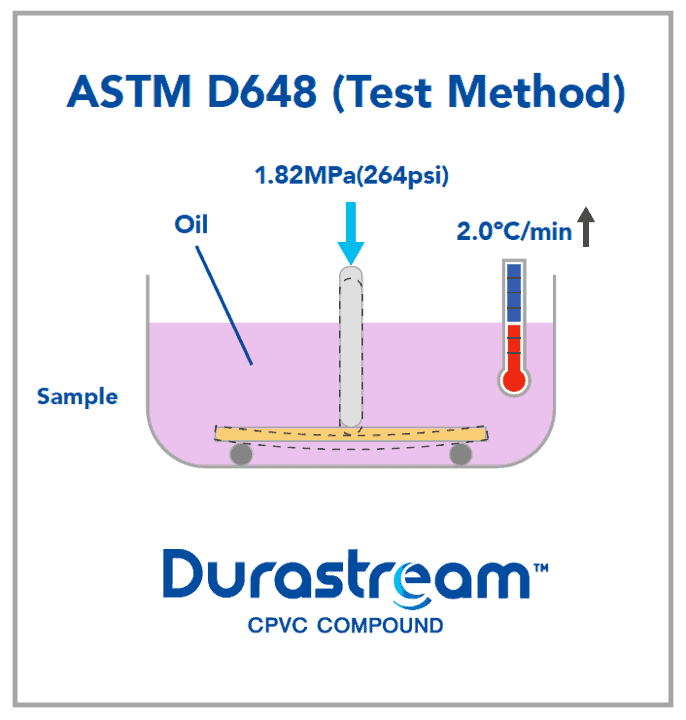
Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) is a very important metric, as it indicates the temperature at which the material will become soft enough to deflect even a small mechanical load. If the temperature stays above HDT, permanent deflection will occur. CPVC generally is used in hot temperature environments since it has one of the highest HDTs among competitive plastics. The table below shows the heat deflection temperature (HDT) as compared to other plastics. While the exact values will differ due to grade and manufacturer, the general trend will remain true: CPVC compound has one of the highest HDTs in the plastics industry.
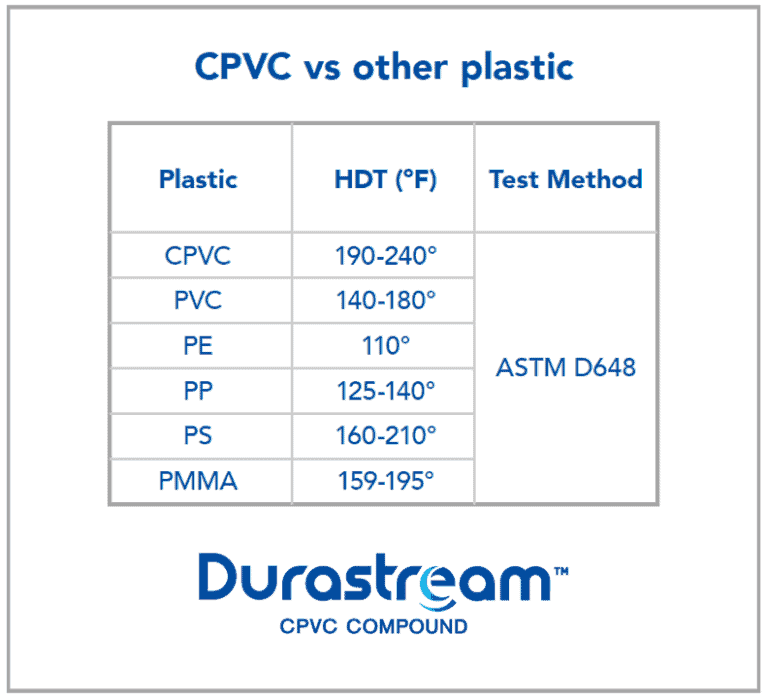
References for HDT data:
SEKISUI internal test data 2. The Chemical Society of Japan
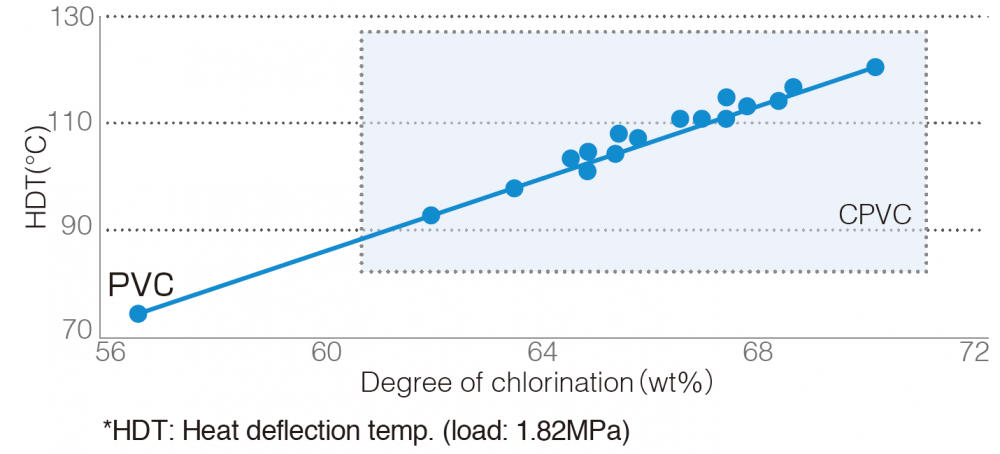
The HDT improves in correlation with the chlorine content in CPVC compound. As can be seen in the chart below, as the chlorine content increases, so does the HDT. SEKISUI produces a wide variety of CPVC compounds to meet the various needs of each application.
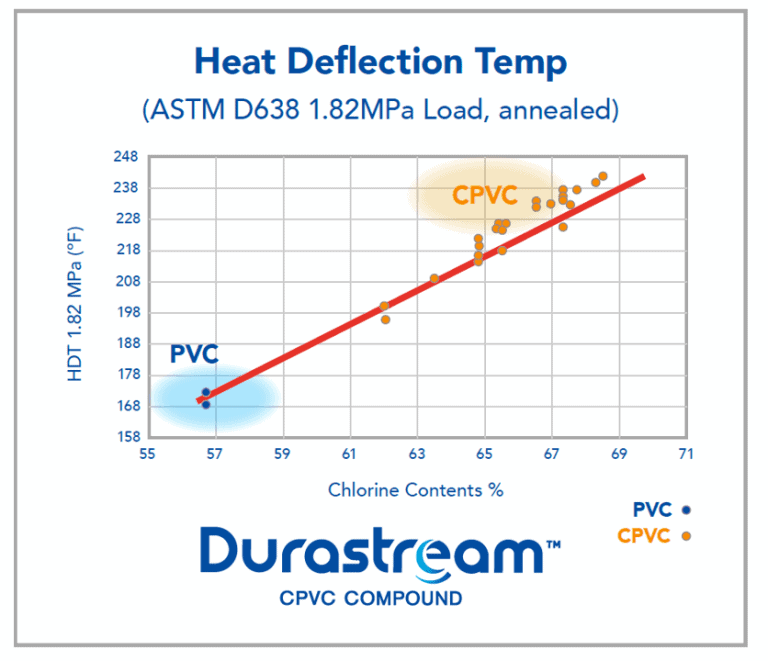
The heat deflection temperature is 10℃ to 40℃ higher than that of PVC
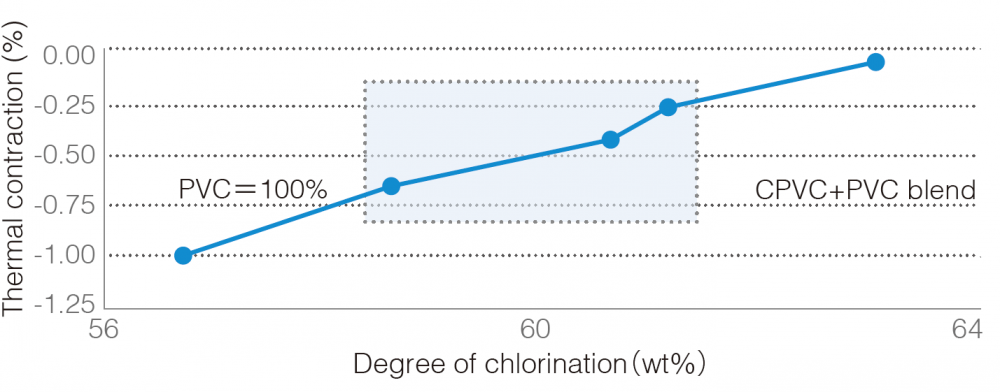
Superior thermal contraction properties at high temperatures due to improved heat resistance.